Migration Strategies: Business Guide
📋 Strategy Overview: Choosing Your Path to the Cloud
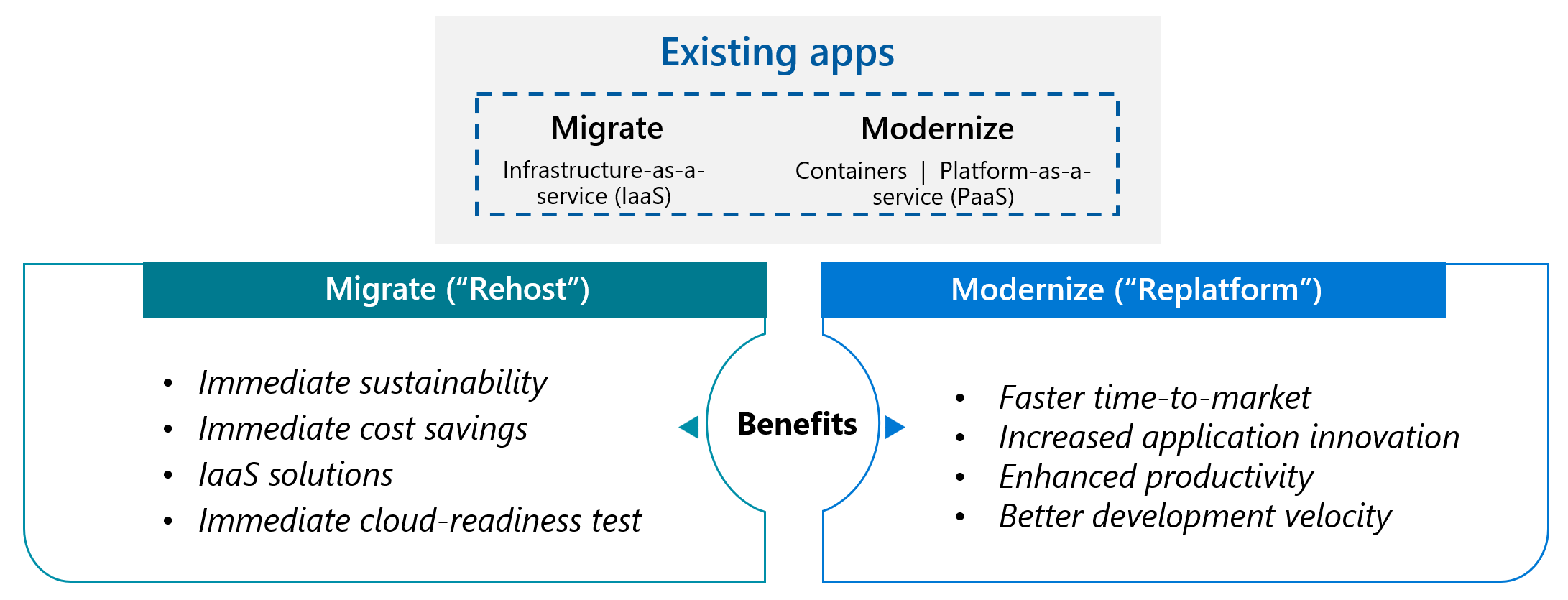
Selecting the right migration strategy is critical to meeting your business objectives while minimizing risk and disruption. This guide provides a business-focused overview of the two primary migration strategies: Rehost and Refactor.
Executive Insight: “The fastest path to the cloud isn’t always the best for your business goals. Choose your migration strategy based on your specific business outcomes, timeline constraints, and application characteristics.”
🚚 Rehost: Lift and Shift
Rehosting moves your existing systems to Azure with minimal changes—often called “lift and shift.” This approach prioritizes speed and risk reduction over cloud optimization.
Business Benefits
| Benefit | Metrics | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Speed to Market | 30-50% faster migration | Quicker realization of basic cloud benefits like exit from datacenter |
| Risk Reduction | 60% fewer migration issues | Lower business disruption during migration |
| Cost Efficiency | 20-30% infrastructure savings | Immediate reduction in capital expenses |
| Minimal Retraining | Near-zero learning curve | Existing staff can manage systems without extensive retraining |
Ideal Business Scenarios
- Datacenter Exit: When you need to vacate a physical datacenter quickly
- Capital Expense Reduction: When you need to eliminate hardware refresh cycles
- Low-Risk First Steps: For organizations new to cloud adoption
- Legacy Systems: For applications that function well but need cloud infrastructure benefits
Implementation Timeline
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Business Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | 1-2 weeks | • Inventory systems • Compatibility checking |
✓ Migration candidate list ✓ Sizing requirements |
| Planning | 1-3 weeks | • Resource planning • Network design • Security mapping |
✓ Target architecture ✓ Migration plan ✓ Cost projections |
| Migration | 2-8 weeks | • VM replication • Test migrations • Cutover planning |
✓ Working cloud environment ✓ Validated applications |
| Optimization | Ongoing | • Performance tuning • Cost optimization |
✓ Optimized cloud spend ✓ Performance baselines |
Real-World Example: “A financial services company migrated 1,200 VMs to Azure using a rehost strategy, completing their datacenter exit 4 months ahead of schedule and reducing infrastructure costs by 28% in the first year.”
🔄 Refactor: Modernize Key Components
Refactoring involves making targeted changes to your applications to better leverage cloud capabilities, without completely rebuilding them. This approach balances modernization benefits with pragmatic implementation timelines.
Business Benefits
| Benefit | Metrics | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Optimization | 30-50% operational savings | Better utilization of cloud-native services reduces ongoing costs |
| Improved Scalability | 200-300% better peak handling | Better customer experience during high-demand periods |
| Enhanced Reliability | 99.95%+ availability | Fewer outages and business disruptions |
| Operational Efficiency | 40% less management overhead | IT teams spend less time on maintenance, more on innovation |
Ideal Business Scenarios
- Performance Bottlenecks: When current system performance is limiting business growth
- Cost Challenges: When operating costs for current systems are too high
- Competitive Pressure: When you need to improve customer experience or time-to-market
- Modernization Steps: When taking an incremental approach to full application modernization
Implementation Timeline
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Business Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | 2-3 weeks | • Application analysis • Dependency mapping • Modernization opportunities |
✓ Refactoring targets ✓ Expected business outcomes |
| Planning | 2-4 weeks | • Target architecture • Service selection • Refactoring scope |
✓ Detailed refactoring plan ✓ Risk mitigation strategy |
| Implementation | 4-12 weeks | • Code modifications • Service integration • Testing |
✓ Modernized application components ✓ Improved capabilities |
| Optimization | Ongoing | • Performance monitoring • Further refactoring |
✓ Continuous improvement ✓ Increasing cloud ROI |
Real-World Example: “A retail company refactored their e-commerce platform’s database tier to Azure SQL and caching layer to Azure Redis Cache, resulting in 45% faster page load times and a 23% increase in conversion rates during their seasonal sales events.”
🔍 Strategy Comparison: Making the Right Choice
| Consideration | Rehost | Refactor |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Value | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Fastest option |
⭐⭐⭐ Requires some development time |
| Risk Level | ⭐ Lowest risk option |
⭐⭐ Moderate risk with proper testing |
| Cost Savings | ⭐⭐ Initial savings, but less optimized |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Better long-term economics |
| Cloud Benefits | ⭐⭐ Basic infrastructure benefits |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Leverages more cloud capabilities |
| Operational Change | ⭐ Minimal process changes |
⭐⭐⭐ Requires some operational adjustments |
| Future Flexibility | ⭐⭐ Limited optimization potential |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Better foundation for future innovation |
Decision Framework
Ask these questions to determine which strategy best fits your business needs:
- Timeline Pressure: How quickly do you need to be in the cloud?
- Immediate need → Rehost
- Can invest some time → Refactor
- Application Criticality: How important is the application to your business?
- Supporting systems → Often Rehost
- Core business applications → Consider Refactor
- Current Performance: Are you experiencing issues with the current system?
- Performs adequately → Rehost may suffice
- Performance problems → Refactor likely needed
- Resource Availability: Do you have development resources available?
- Limited development capacity → Rehost
- Development team available → Refactor is viable
- Business Growth: Are you anticipating significant business growth?
- Stable business needs → Rehost may be adequate
- Growth or variability expected → Refactor for scalability
Pro Tip: “Many successful cloud migrations use a hybrid approach, rehosting some applications while refactoring the most critical or problematic components to maximize ROI.”
📈 Measuring Success: Key Business Metrics
| Metric Category | Rehost Metrics | Refactor Metrics | Target Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | • Infrastructure cost reduction • CAPEX to OPEX shift |
• Total cost of ownership • Resource utilization efficiency |
20-40% reduction |
| Performance | • System availability • Basic response times |
• Application throughput • End-user experience metrics |
15-45% improvement |
| Agility | • Provisioning time reduction • Deployment frequency |
• Feature delivery time • Business process improvement |
30-60% faster |
| Risk | • Successful DR tests • Security compliance |
• Reduced technical debt • Automated recovery |
50-70% risk reduction |
🔄 Next Steps
- Conduct Application Assessment:
- Inventory all applications and infrastructure
- Score applications on business value and modernization complexity
- Identify initial candidates for each strategy
- Build Your Business Case:
- Calculate expected TCO for each approach
- Define clear success metrics aligned with business goals
- Set realistic timelines and resource requirements
- Create a Phased Approach:
- Start with lower-risk applications to build experience
- Plan waves that group similar applications or dependencies
- Build a feedback loop to apply learnings to subsequent waves
Executive Decision Point: Consider starting with a rehosting approach for non-critical systems while refactoring your most important business applications in parallel. This balanced approach delivers quick wins while building toward optimal long-term solutions.